acl and pcl tear test|difference between acl and pcl : exporters McMurray Test The McMurray test is performed with the patient supine and the examiner grasping the medial aspect of the affected knee with one hand and the patient’s heel with . See more The PR140 pressure data logger and the temperature only HiTemp140 are IP68 fully submersible and are specifically designed for autoclave and steriliser validation. Each data logger has 32,000 memory points and a solid state .
{plog:ftitle_list}
PAE tubing is manufactured specifically for medium and high pressure applications requiring both strength and corrosion resistance. The tubing is furnished in random lengths between 20 and .
Lacchman’s test It is performed with the patient supine and the knee flexed 20–30°. The examiner grasps the distal femur (from lateral side) with one hand and the proximal tibia with the other hand (from medial side). The lower leg is given a brisk forward tug in an attempt to identify a discrete endpoint. A . See morePosterior Drawer Test This test is performed with the patient supine and the knee flexed to 90°. There are two different ways it may be . See moreMcMurray Test The McMurray test is performed with the patient supine and the examiner grasping the medial aspect of the affected knee with one hand and the patient’s heel with . See more
Valgus stress test for Medial Collateral Ligament It is performed with the patient supine and the knee in 20° of flexion. With one hand on the lateral aspect of the knee and the other on the foot, the examiner gently abducts and externally rotates the lower leg. Increased . See more The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) are two major ligaments in the knee that work together to provide stability. They are also common sites . PCL injuries are traumatic knee injuries that may lead to posterior knee instability and often present in combination with other ipsilateral ligamentous knee injuries (i.e PLC, ACL). Diagnosis can be suspected clinically with a . Varus stress test for Lateral Collateral Ligament. In the varus stress test, the examiner adducts and internally rotates the lower leg to assess the stability of the lateral .
The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) are two major ligaments in the knee that work together to provide stability. They are also common sites . The anterior drawer test is a physical examination doctors use to test the stability of the knee’s anterior cruciate ligament (ACL). Doctors may use this test, along with images and .The Lachman test is a passive accessory movement test of the knee performed to identify the integrity of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL). The test is designed to assess single and . PCL injuries are traumatic knee injuries that may lead to posterior knee instability and often present in combination with other ipsilateral ligamentous knee injuries (i.e PLC, .
ACL tears are common athletic injuries leading to anterior and lateral rotatory instability of the knee. Diagnosis can be suspected clinically with presence of a traumatic knee . Diagnosis. During the physical exam, your doctor will check your knee for swelling and tenderness — comparing your injured knee to your uninjured knee. He or she may also .
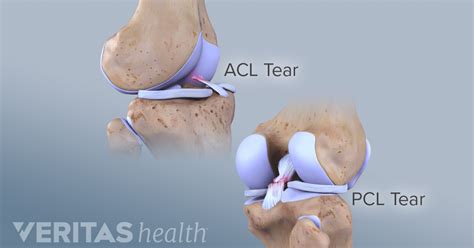
The PCL is closer to the back of your knee. Your ACL is like a strap that connects your bones and prevents your knee from bending or rotating too much. Anything that puts . The ACL and the posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) together form a cross (or an “x”) within the knee and prevent excessive forward or backward motion of the tibia relative to . anterior cruciate ligament. ( ACL. ), posterior cruciate ligament. ( PCL. ), medial collateral ligament. ( MCL. ), and. lateral collateral ligament. ( LCL. ) result in knee pain and .
Varus stress test for Lateral Collateral Ligament. In the varus stress test, the examiner adducts and internally rotates the lower leg to assess the stability of the lateral . The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) are two major ligaments in the knee that work together to provide stability. They are also common sites . The anterior drawer test is a physical examination doctors use to test the stability of the knee’s anterior cruciate ligament (ACL). Doctors may use this test, along with images and .
The Lachman test is a passive accessory movement test of the knee performed to identify the integrity of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL). The test is designed to assess single and .
PCL injuries are traumatic knee injuries that may lead to posterior knee instability and often present in combination with other ipsilateral ligamentous knee injuries (i.e PLC, . ACL tears are common athletic injuries leading to anterior and lateral rotatory instability of the knee. Diagnosis can be suspected clinically with presence of a traumatic knee .
Diagnosis. During the physical exam, your doctor will check your knee for swelling and tenderness — comparing your injured knee to your uninjured knee. He or she may also .
The PCL is closer to the back of your knee. Your ACL is like a strap that connects your bones and prevents your knee from bending or rotating too much. Anything that puts . The ACL and the posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) together form a cross (or an “x”) within the knee and prevent excessive forward or backward motion of the tibia relative to .
autoclave chamber &
what is a pcl rupture
pcl tear treatment healing time
Who MUST autoclave their infectious waste? See Resources for Biohazardous Waste Disposal for additional guidance for your building or department on proper disposal of Infectious Waste. Autoclaving requirement .
acl and pcl tear test|difference between acl and pcl